Published
-
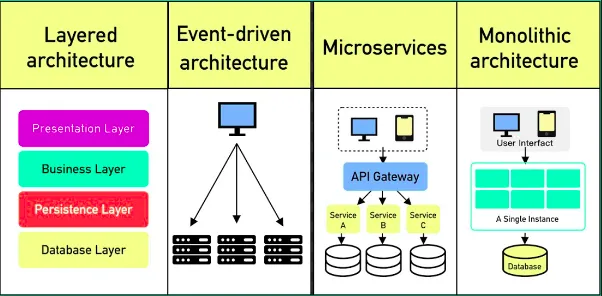
Layered Architecture Pattern

Layered architecture is a way of organizing software into separate levels, or layers, where each layer has a specific role or responsibility.
 Let’s break it down in simple terms
Let’s break it down in simple terms
1. Presentation Layer
- This is like the face of application
- What users see and interact with
- Examples: buttons, screens, forms
2. Business Layer
- This is the brain of your application
- Contains all the rules about how things should work
- Example: calculating total price with tax in a shopping app
3. Persistence Layer
- This is like a translator between app and the database
- Handles how data is saved and loaded
- Example: converting user information into a format that can be saved
4. Database Layer
- This is like a filing cabinet where all data is stored
- Actual storage of information
- Example: storing user accounts, products, orders
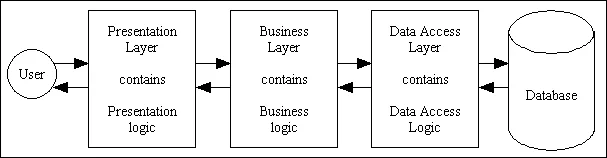
Important Feature
Two-Way Traffic: Information typically flows from top to bottom vice versa, like flight from Bengaluru to Lucknow and Lucknow to Bengaluru
Independence: Each layer can be changed without affecting others.
Organization: Similar things stay together (like keeping all UI elements in the presentation layer)
When to Use This Pattern
- Perfect for simple applications.
- Good for small user bases (less than 200 users).
- Great for projects where requirements won’t change much.
- Ideal for learning and starting out.
Limitations
Speed: Like taking stairs in a tall building, requests must go through each layer, which can be slow.
Changes: Like moving furniture in a full room, making changes can be tricky.
Updates: If you change one layer, you usually need to redeploy the whole application.
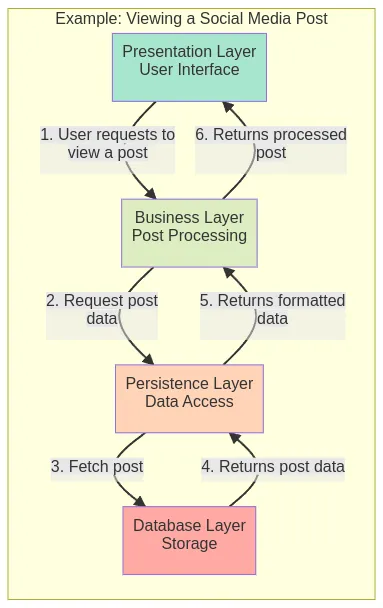
Real Time Example
Some of Software Architecture Patterns