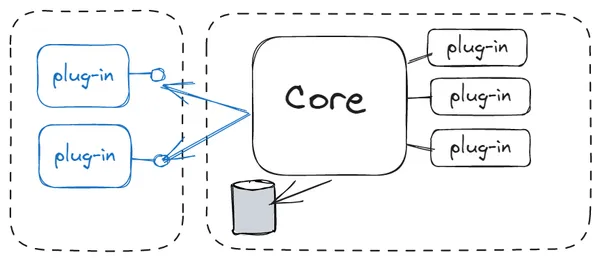
The Microkernel Architecture pattern is a powerful solution for systems that need to be adaptable, extensible, and lightweight. By keeping the core minimal and allowing for extensions through plug-ins, the pattern ensures flexibility while maintaining system stability and performance. However, it requires careful design to manage plug-in complexity and ensure efficient communication between the core and its extensions.







